Study finds evidence of resistance to COVID-19 drugs umnmedschool ScienceAdvances
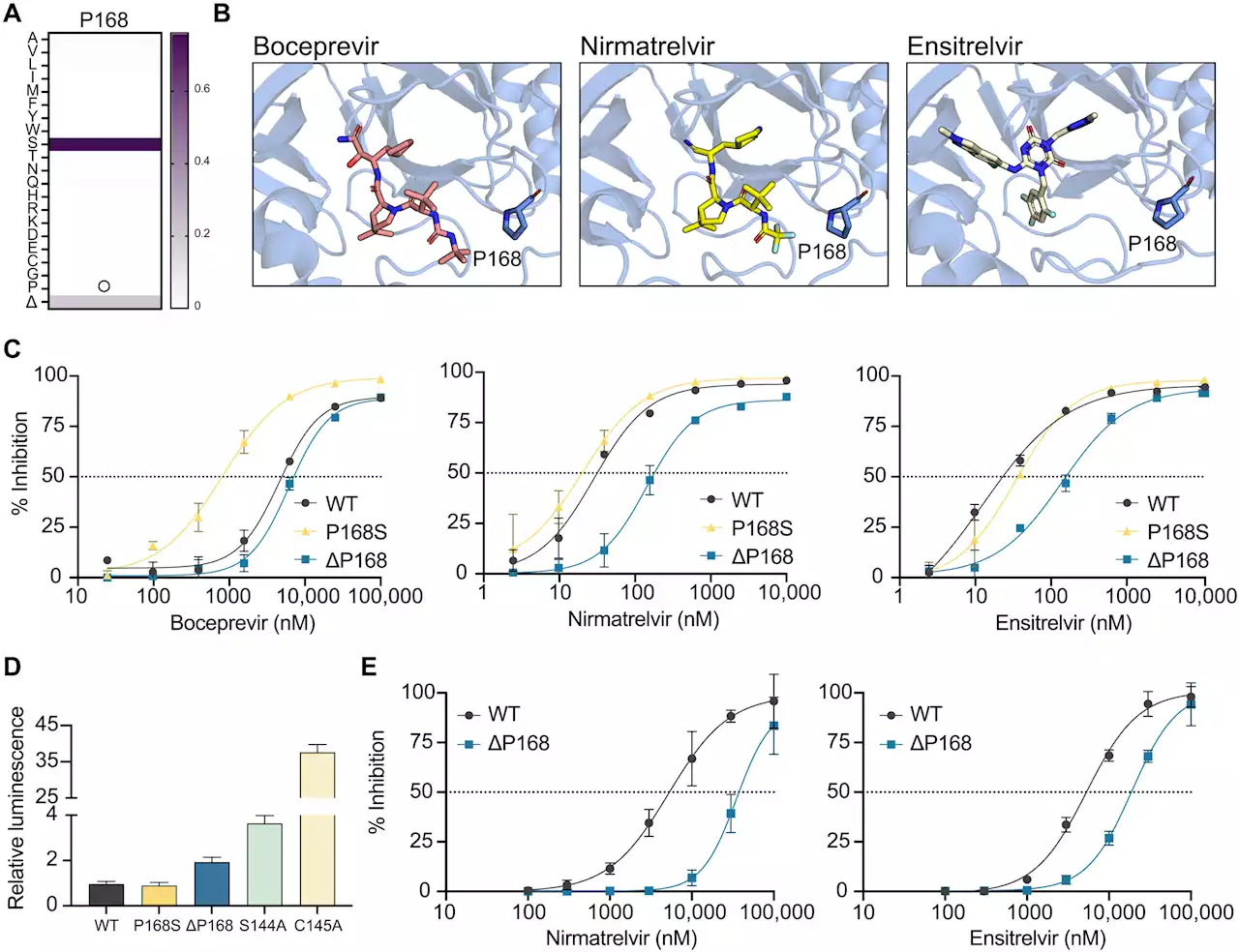
nirmatrelvir, the active component of Paxlovid, the study found that a different set of mutations currently in circulation can transfer resistance to ensitrelvir , a protease inhibitor now approved in Japan. This new research shows that simple single amino acid changes in SARS-CoV-2 main protease could severely undermine efficacy of these antiviral drugs.
Further research is likely to develop additional next-generation protease inhibitors with different resistance profiles, as well as drugs that target different viral processes such as replication or cell entry. A multi-approach—like existing therapies for HIV and Hepatitis C virus—could further help to protect against resistance and cure SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals.
"Despite Paxlovid's proven success in blunting COVID-19 symptoms, the long-term consequences of its widespread use in speeding up resistance are unknown," said S. Arad Moghadasi, co-author of the study and a University of Minnesota Medical School graduate student."Drugs with the highest barriers to resistance are likely to prove more effective and have longer-term durability.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 New study suggests broad neutralizing antibody could provide three years of COVID protectionIn a recent article published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers showed that a novel, lab-engineered monoclonal antibody (mAb), adintrevimab conferred up to 50% protection against symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, it demonstrated this exceptional efficacy in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–naïve individuals even at titers as low as 1:30.
New study suggests broad neutralizing antibody could provide three years of COVID protectionIn a recent article published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers showed that a novel, lab-engineered monoclonal antibody (mAb), adintrevimab conferred up to 50% protection against symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, it demonstrated this exceptional efficacy in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–naïve individuals even at titers as low as 1:30.
Weiterlesen »
 Study links altered gut microbiome to allergies in infants raised under COVID-19 lockdownStudy links altered gut microbiome to allergies in infants raised under COVID-19 lockdown Microbiome Coronavirus Disease COVID Allergies medrxivpreprint helsinkiuni UCC RCSI_Irl CHI_Ireland karolinskainst CUMedicalSchool
Study links altered gut microbiome to allergies in infants raised under COVID-19 lockdownStudy links altered gut microbiome to allergies in infants raised under COVID-19 lockdown Microbiome Coronavirus Disease COVID Allergies medrxivpreprint helsinkiuni UCC RCSI_Irl CHI_Ireland karolinskainst CUMedicalSchool
Weiterlesen »
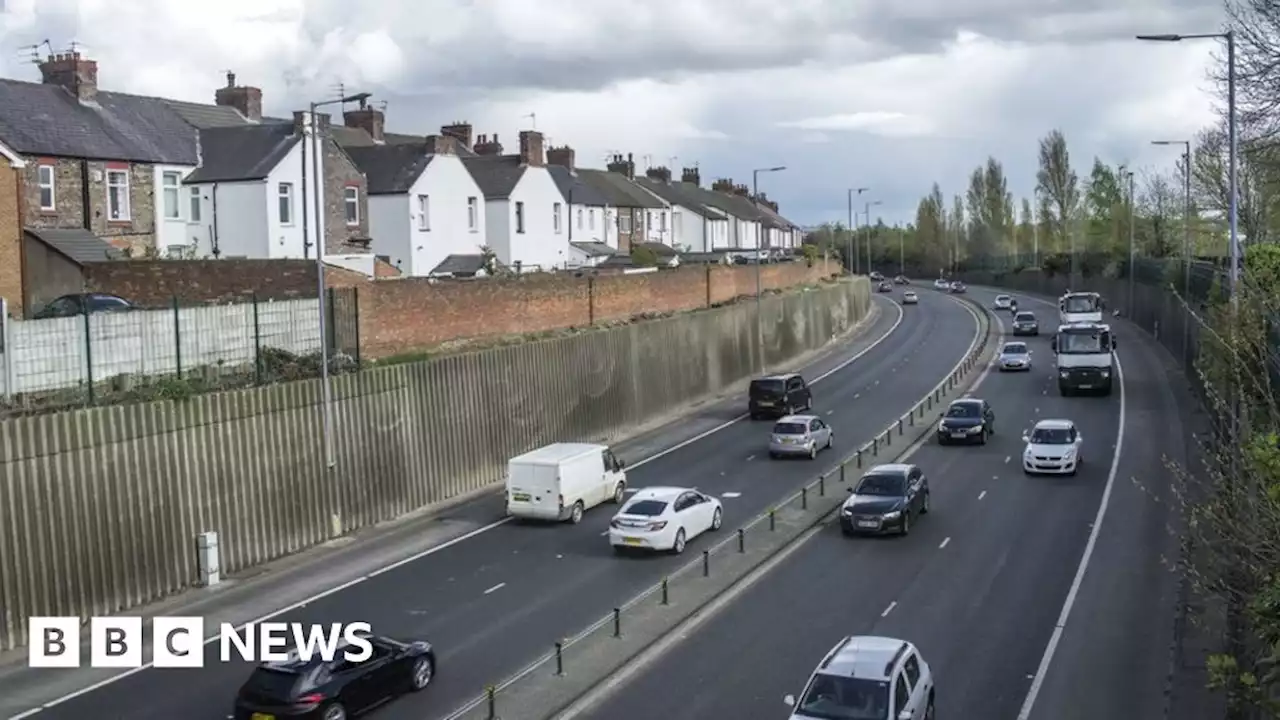 Road noise makes blood pressure rise, study findsResearchers say they studied data from more than 240,000 people who lived near noisy roads.
Road noise makes blood pressure rise, study findsResearchers say they studied data from more than 240,000 people who lived near noisy roads.
Weiterlesen »
 Dementia study finds eating more of one nutrient could help stave off diseaseThose who ate more leafy greens had a younger brain age when they reached 55.
Dementia study finds eating more of one nutrient could help stave off diseaseThose who ate more leafy greens had a younger brain age when they reached 55.
Weiterlesen »
 Smelling other people's sweat could reduce social anxiety, suggests studyApparently, smelling other people’s body odour could provide a calming effect that helps with social anxiety.
Smelling other people's sweat could reduce social anxiety, suggests studyApparently, smelling other people’s body odour could provide a calming effect that helps with social anxiety.
Weiterlesen »
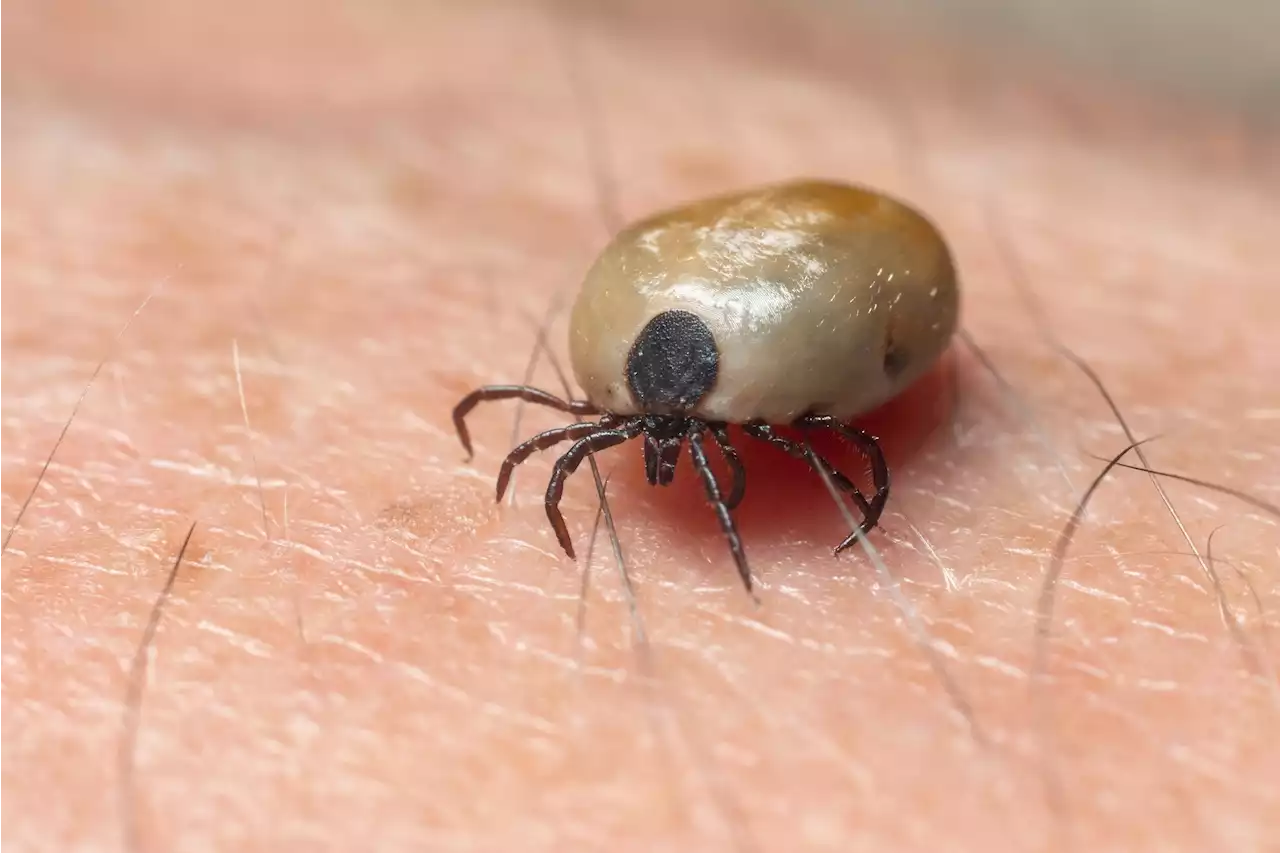 Study details bacterial agents in 418 ticks extracted from humans in FranceIn a recent study published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, researchers analyzed ticks that bit humans between January 2014 and March 2021 in France for the presence of bacterial pathogens.
Study details bacterial agents in 418 ticks extracted from humans in FranceIn a recent study published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, researchers analyzed ticks that bit humans between January 2014 and March 2021 in France for the presence of bacterial pathogens.
Weiterlesen »