'Binocular' treatment followed by sleep found to help with a common vision problem umich CommsBio
. Here, in side-by-side comparison of the effects of brief binocular vs. monocular recovery experiences in mice, we show the two have strikingly different effects on bV1 ocular dominance and network activation in bV1. These data reflect findings using comparisons of 24-h binocular vs. monocular recovery, where simply re-opening the DE in mice was found to be more efficacious for restoring binocular vision than RO.
, we hope that our present data will inform future strategies for optimizing amblyopia treatment in children.All mouse husbandry and experimental/surgical procedures were reviewed and approved by the University of Michigan Internal Animal Care and Use Committee. Weaned C57BL6/J mice were housed in a vivarium under 12 h:12 h light/dark cycles with littermates starting postnatal day 21 and hadaccess to food and water.
For all experiments, male littermates were randomly assigned to treatment groups. For monocular deprivation , mice were anesthetized at P28 using 1–1.5% isoflurane. Nylon non-absorbable sutures were used to occlude the left eye. Sutures were checked twice daily to verify continuous MD; during this time they were handled 5 min/day. After MD , mice were anesthetized with 1–1.5% isoflurane a second time and left eyelid sutures were removed.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Type I interferon shapes brain distribution and tropism of tick-borne flavivirus - Nature CommunicationsHere the authors combine a multimodal imaging-snRNAseq transcriptomics strategy to provide insight into the distribution of a neurotropic tick-borne flavivirus in the brain, and show that absence of interferon signaling increases infection of resident microglia.
Type I interferon shapes brain distribution and tropism of tick-borne flavivirus - Nature CommunicationsHere the authors combine a multimodal imaging-snRNAseq transcriptomics strategy to provide insight into the distribution of a neurotropic tick-borne flavivirus in the brain, and show that absence of interferon signaling increases infection of resident microglia.
Weiterlesen »
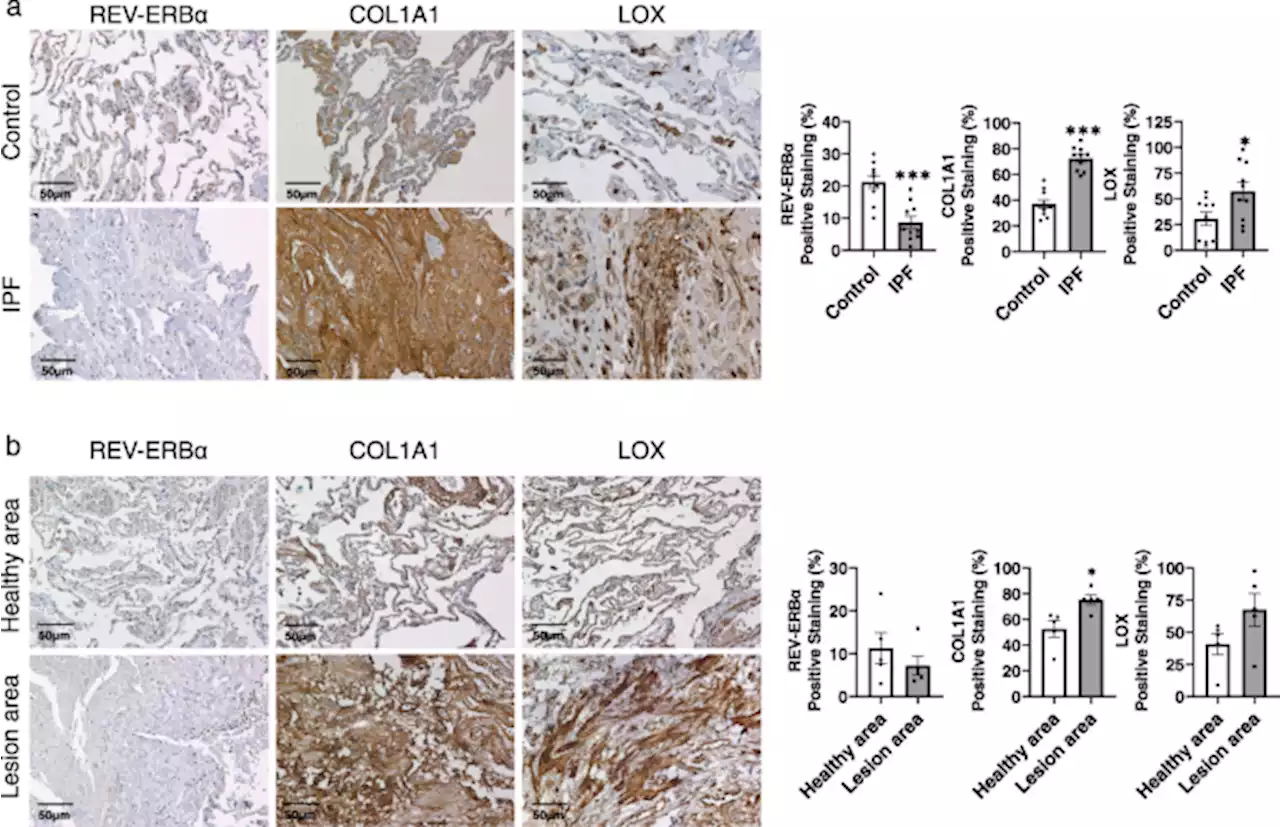 Circadian clock molecule REV-ERBα regulates lung fibrotic progression through collagen stabilization - Nature CommunicationsThe molecular clock REV-ERBα regulates lung injury during fibrosis, but the role of REV-ERBα in fibrogenesis remains unknown. Here, the authors show that REV-ERBα interacts with the lysyl oxidase-collagen axis during fibrogenesis and demonstrate the therapeutic potential of Rev-erbα agonist against lung fibrosis.
Circadian clock molecule REV-ERBα regulates lung fibrotic progression through collagen stabilization - Nature CommunicationsThe molecular clock REV-ERBα regulates lung injury during fibrosis, but the role of REV-ERBα in fibrogenesis remains unknown. Here, the authors show that REV-ERBα interacts with the lysyl oxidase-collagen axis during fibrogenesis and demonstrate the therapeutic potential of Rev-erbα agonist against lung fibrosis.
Weiterlesen »
 The usherin mutation c.2299delG leads to its mislocalization and disrupts interactions with whirlin and VLGR1 - Nature CommunicationsThe c.2299delG mutation in usherin causes loss of hearing and vision. Here, the authors show in a mouse model of this disease that the expression of mutant usherin leads to retinitis pigmentosa and structural defects in the photoreceptor cilium associated with mislocalization of VLGR1 and WHRN.
The usherin mutation c.2299delG leads to its mislocalization and disrupts interactions with whirlin and VLGR1 - Nature CommunicationsThe c.2299delG mutation in usherin causes loss of hearing and vision. Here, the authors show in a mouse model of this disease that the expression of mutant usherin leads to retinitis pigmentosa and structural defects in the photoreceptor cilium associated with mislocalization of VLGR1 and WHRN.
Weiterlesen »
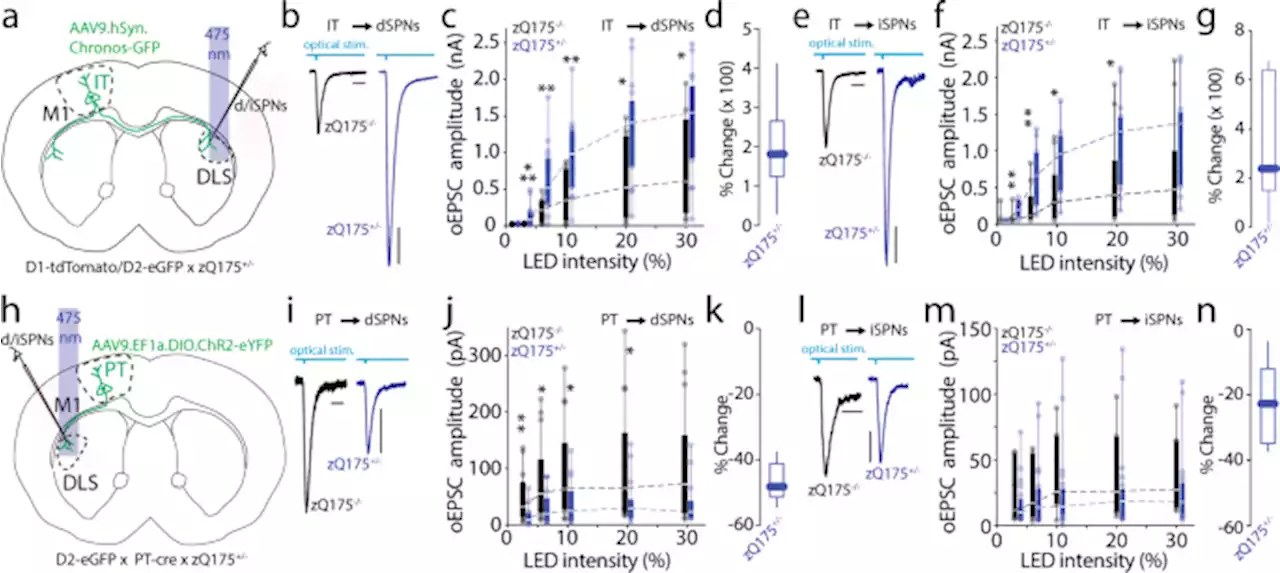 Cholinergic deficits selectively boost cortical intratelencephalic control of striatum in male Huntington’s disease model mice - Nature CommunicationsThe corticostriatal dysfunction underlying Huntington’s disease remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors find increased intratelencephalic connectivity resulting from deficient cholinergic transmission in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease.
Cholinergic deficits selectively boost cortical intratelencephalic control of striatum in male Huntington’s disease model mice - Nature CommunicationsThe corticostriatal dysfunction underlying Huntington’s disease remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors find increased intratelencephalic connectivity resulting from deficient cholinergic transmission in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease.
Weiterlesen »
 A ferritin-based COVID-19 nanoparticle vaccine that elicits robust, durable, broad-spectrum neutralizing antisera in non-human primates - Nature CommunicationsHere the authors develop a ferritin-based protein nanoparticle vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2, and show induction of neutralizing antibodies to variants of concern, including Omicron BQ.1, in non-human primates after initial immunization and a booster dose.
A ferritin-based COVID-19 nanoparticle vaccine that elicits robust, durable, broad-spectrum neutralizing antisera in non-human primates - Nature CommunicationsHere the authors develop a ferritin-based protein nanoparticle vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2, and show induction of neutralizing antibodies to variants of concern, including Omicron BQ.1, in non-human primates after initial immunization and a booster dose.
Weiterlesen »
