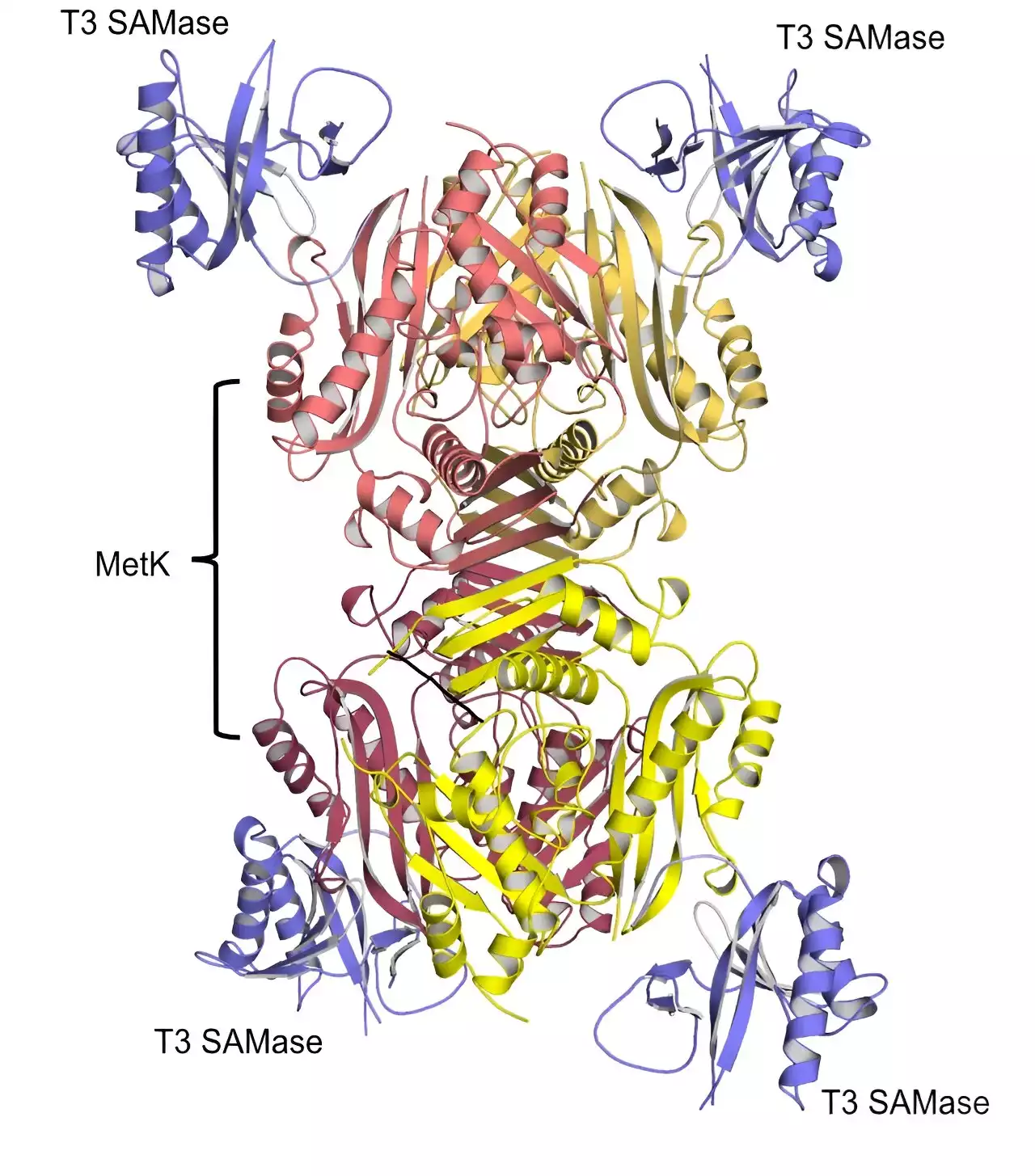
Scientists from Skoltech and research centers in Sweden and Switzerland have presented results that explain the mechanism of interaction between bacteria and phages—viruses that infect bacterial cells. The discovery is an important step on the way to developing new ways to fight infections. The study is published in the journalCell Reports.
, have a natural origin, and can be found wherever there is life and bacteria. Phages had been studied more than 100 years ago, but when antibiotics were discovered, research interest declined.
"Molecular mechanisms for most of those systems have not been uncovered yet, so one of the ways to learn how microbial immunity works is to find out how viruses managed to overcome the defense. The interaction between viruses and bacteria can be described as an arms race: when bacteria acquire a new defense strategy, it exerts great pressure on the opposing side—"It initiates a new stage of bacterial adaptation, and such intense competition leads to a wide variety of antiviral systems.
"SAM is used as a donor of methyl groups, which can regulate the expression of genes. In the case of the BREX system, a methyl group also serves as a label, which allows bacteria to distinguish between their own DNA and the non-methylated DNA of the virus.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Upcycled plastic can be turned into soap, researchers findMore than 60 million plastic water bottles go into landfills and incinerators every day, according to the Container Recycling Institute.
Upcycled plastic can be turned into soap, researchers findMore than 60 million plastic water bottles go into landfills and incinerators every day, according to the Container Recycling Institute.
Weiterlesen »
 Researchers characterize influenza adaptation to human epithelial cells, with surprising resultsThe 1968 influenza pandemic was caused by the H3N2 flu strain and killed between 1 and 4 million people globally. For the sake of comparison, the WHO estimates that around 3 million people died of COVID-related illness in the year 2020.
Researchers characterize influenza adaptation to human epithelial cells, with surprising resultsThe 1968 influenza pandemic was caused by the H3N2 flu strain and killed between 1 and 4 million people globally. For the sake of comparison, the WHO estimates that around 3 million people died of COVID-related illness in the year 2020.
Weiterlesen »
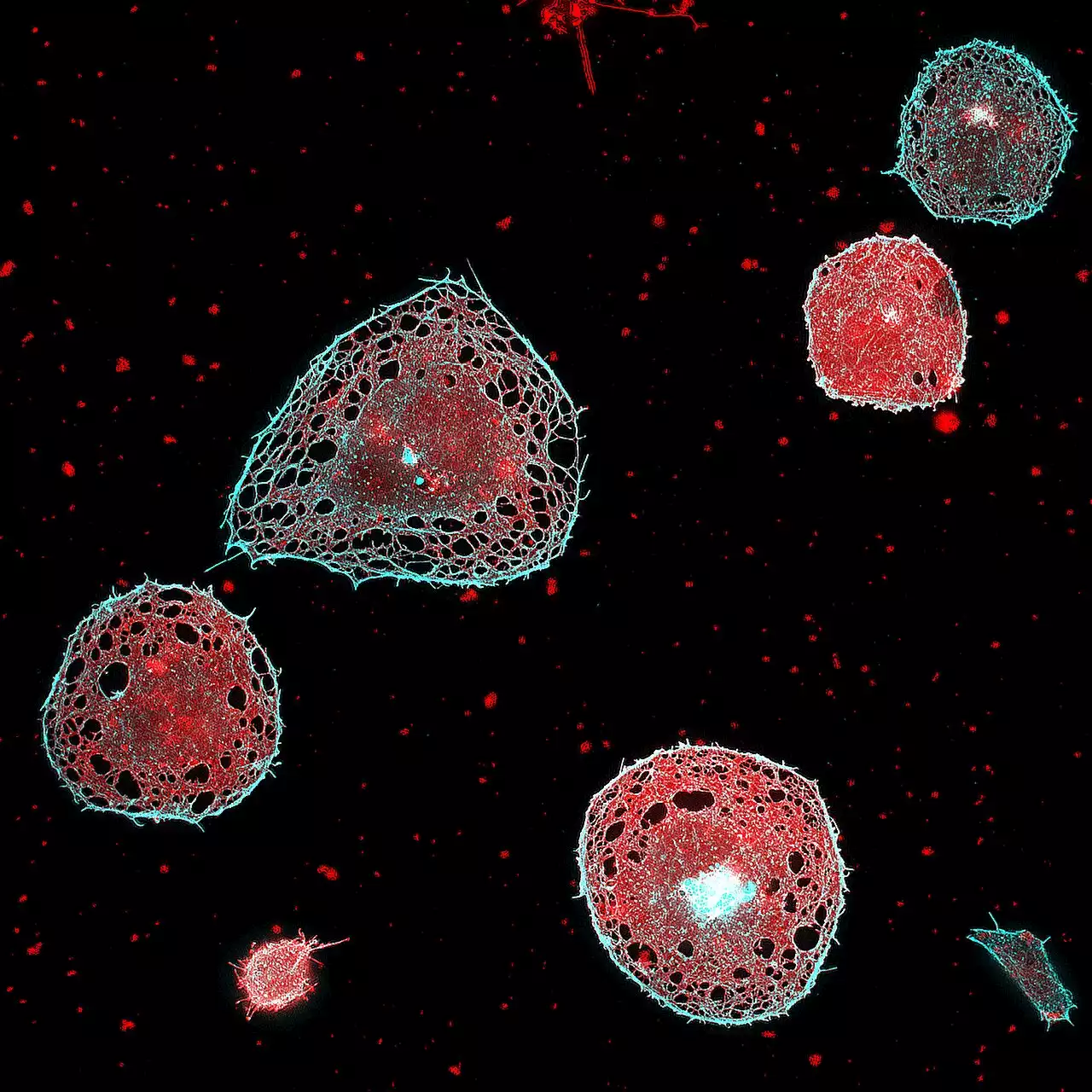 Researchers achieve high-speed super-resolution imaging with a large field of viewResearchers have developed a fluorescence microscope that uses structured illumination for fast super-resolution imaging over a wide field of view. The new microscope was designed to image multiple living cells simultaneously with a very high resolution to study the effects of various drugs and mixtures of drugs on the body.
Researchers achieve high-speed super-resolution imaging with a large field of viewResearchers have developed a fluorescence microscope that uses structured illumination for fast super-resolution imaging over a wide field of view. The new microscope was designed to image multiple living cells simultaneously with a very high resolution to study the effects of various drugs and mixtures of drugs on the body.
Weiterlesen »
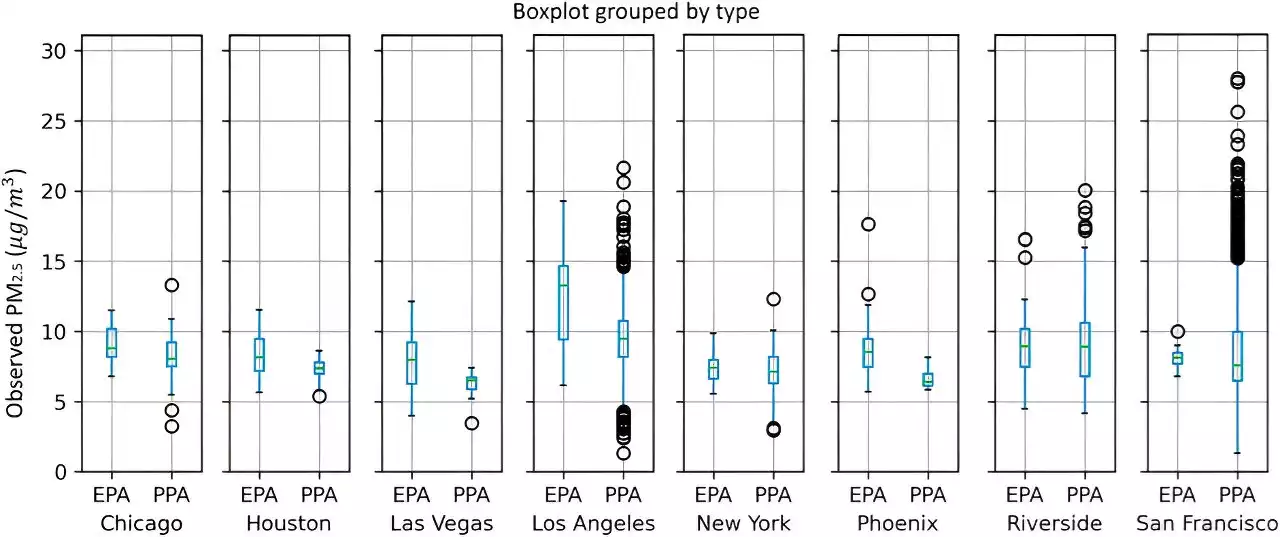 Researchers improve air pollution exposure models using artificial intelligence and mobility dataAmericans in the Northeast paid greater attention to air quality alerts this summer as wildfire smoke thickened skies with an orange-tinted haze. Smoke and other sources of air pollution contain tiny particles, called fine particulate matter (PM 2.5). Smaller than the width of a human hair, PM 2.5 pose health dangers when inhaled, especially to people with pre-existing heart and lung conditions.
Researchers improve air pollution exposure models using artificial intelligence and mobility dataAmericans in the Northeast paid greater attention to air quality alerts this summer as wildfire smoke thickened skies with an orange-tinted haze. Smoke and other sources of air pollution contain tiny particles, called fine particulate matter (PM 2.5). Smaller than the width of a human hair, PM 2.5 pose health dangers when inhaled, especially to people with pre-existing heart and lung conditions.
Weiterlesen »
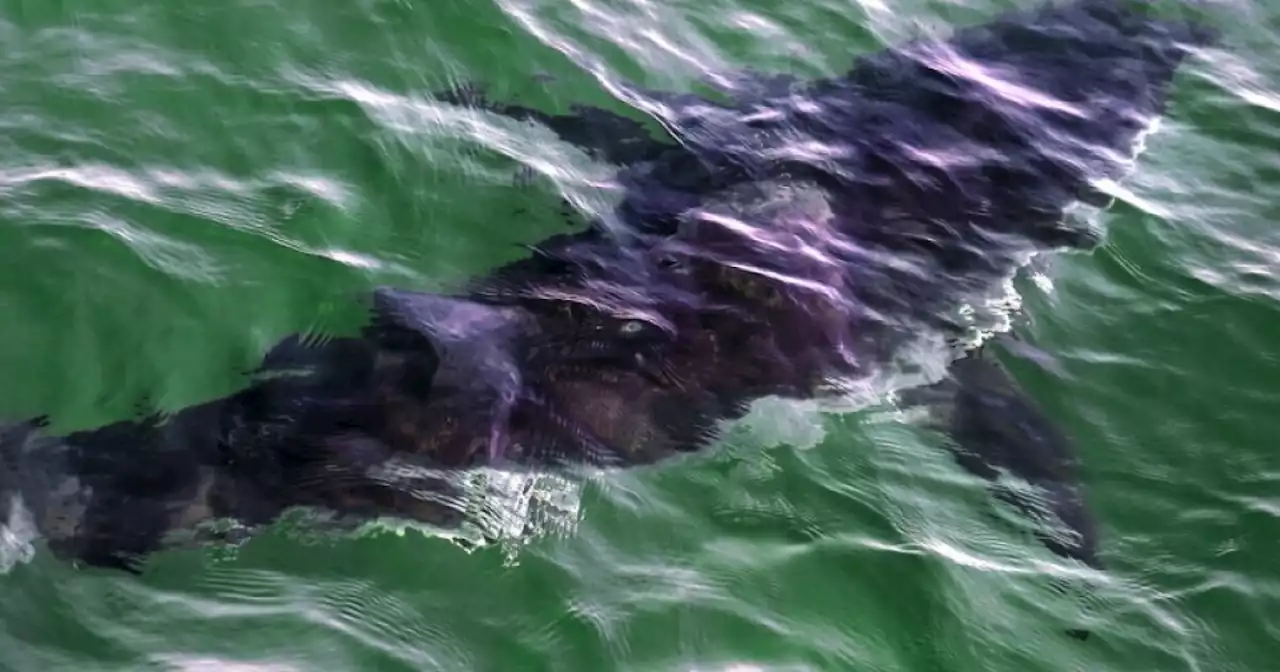 As shark sightings rise, researchers are better understanding speciesIncreased great white shark research is being done ahead of a busy tourist season along the East Coast.
As shark sightings rise, researchers are better understanding speciesIncreased great white shark research is being done ahead of a busy tourist season along the East Coast.
Weiterlesen »
 Elon Musk’s Twitter Takeover Sparked an Exodus of Climate Voices, Researchers FindX, formerly Twitter, has seen a rise in harassment and misinformation, pushing out progressive, climate-minded account users.
Elon Musk’s Twitter Takeover Sparked an Exodus of Climate Voices, Researchers FindX, formerly Twitter, has seen a rise in harassment and misinformation, pushing out progressive, climate-minded account users.
Weiterlesen »