Commercially available mass spectrometers can be reliably used to detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, according to research from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). In a study recently published in Clinical Proteomics, the researchers introduce a novel method that leverages equipment
Researchers have developed a method using commercially available mass spectrometers to detect SARS-CoV-2 in just two hours. The technique, utilizing MALDI-TOF spectrometry, is rapid and adaptable for detecting other pathogens, though it’s not as sensitive as the PCR test.coronavirus, according to research from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg .
The new method requires a nasal or throat swab. The sample needs to be prepared before it can be analyzed by a mass spectrometer, which takes only a few seconds. In MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, a laser pulse is used to transfer the sample to the gas phase – then the mass of the individual components is measured.particles of the coronavirus.
“In acute phases, the method would make an ideal addition to PCR because we would be able to analyze a lot of samples very quickly. Rapid and reliable results may make it easier to contain outbreaks,” explains Lydia Kollhoff, lead author of the study. Moreover, the approach could be adapted rather easily to other pathogens in future pandemics and supplement PCR testing.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Researchers develop a sustainable gel film to capture carbon dioxide with reduced energy costGlobal CO2 emissions for 2022 reached 36.1 gigatons, and this consumed 13–36% of the remaining carbon budget to limit warming to 1.5°C, which means our permissible emissions could be depleted within two years.
Researchers develop a sustainable gel film to capture carbon dioxide with reduced energy costGlobal CO2 emissions for 2022 reached 36.1 gigatons, and this consumed 13–36% of the remaining carbon budget to limit warming to 1.5°C, which means our permissible emissions could be depleted within two years.
Weiterlesen »
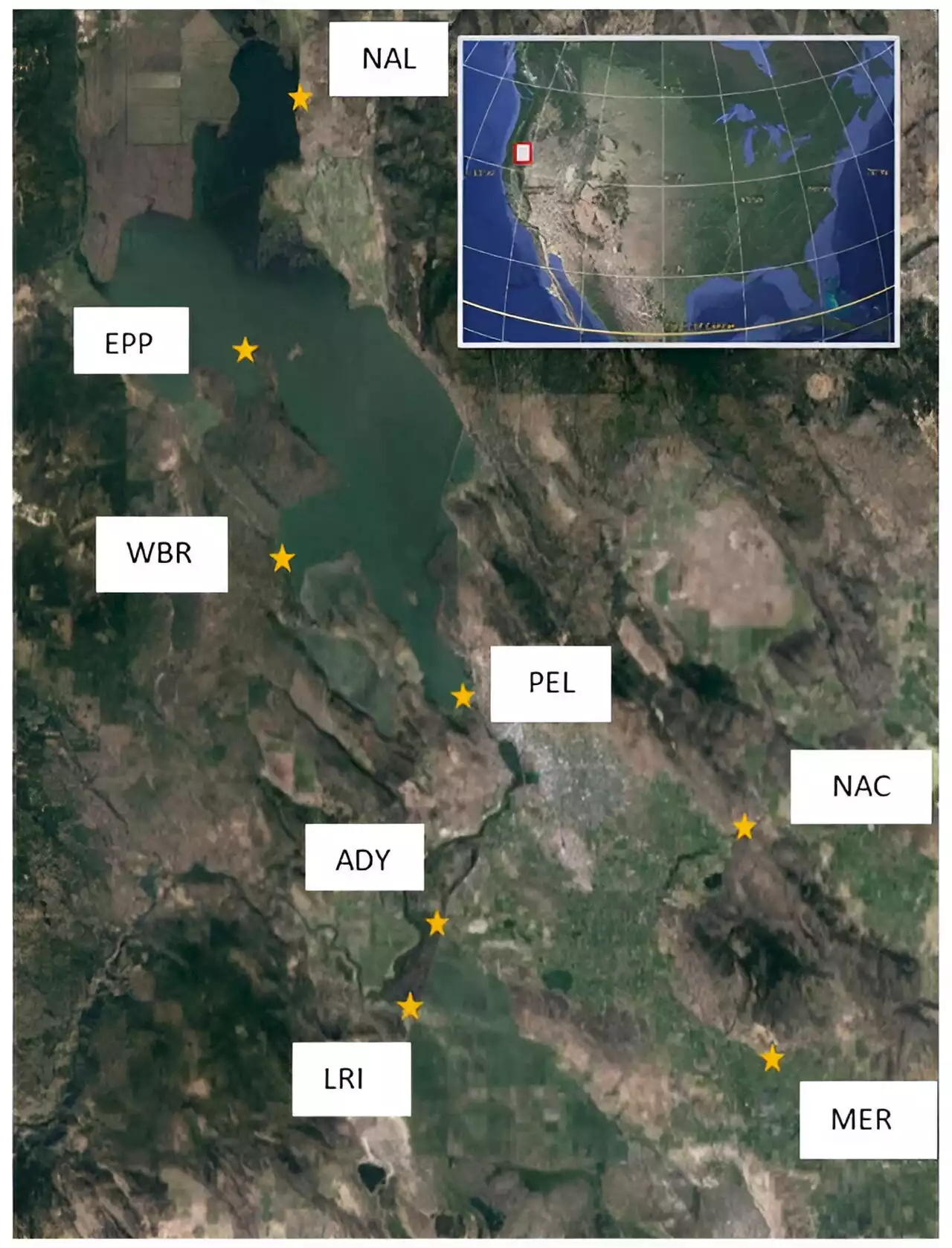 Researchers develop novel technique for sniffing out toxic algae bloomsResearchers at Oregon State University have developed a new way to monitor the danger associated with algae blooms: 'sniffing' the water for gases associated with toxins.
Researchers develop novel technique for sniffing out toxic algae bloomsResearchers at Oregon State University have developed a new way to monitor the danger associated with algae blooms: 'sniffing' the water for gases associated with toxins.
Weiterlesen »
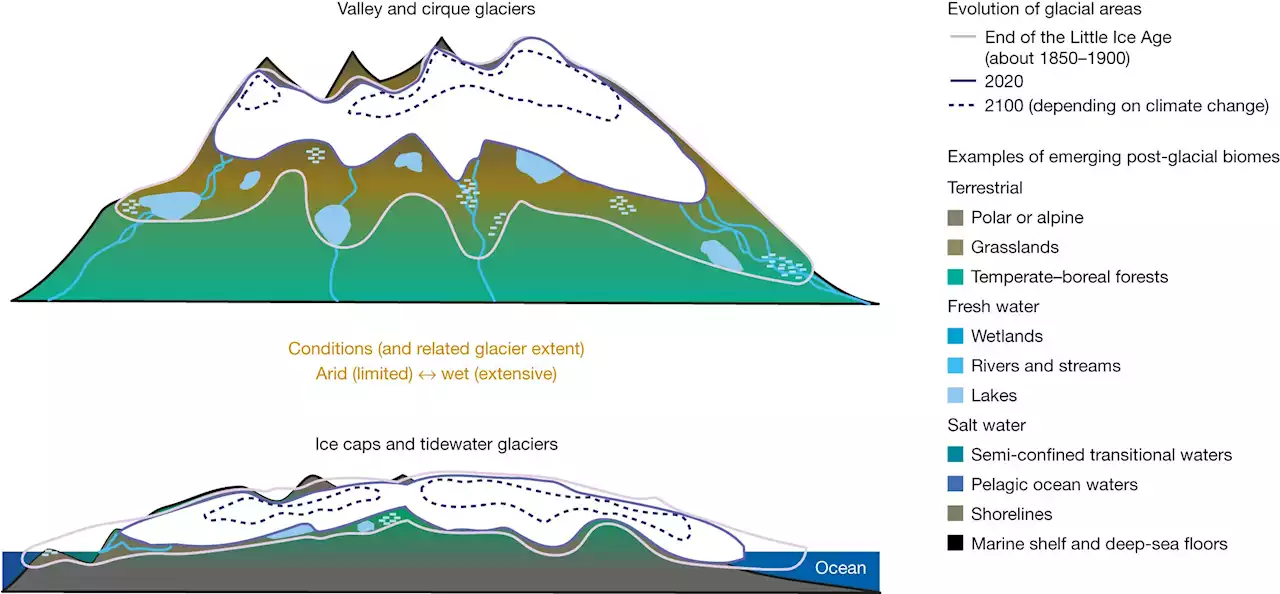 Modeling the future of glaciers and the new ecosystems that will develop as deglaciation occursA team of geologists and geoscientists affiliated with several institutions in Switzerland and two in France, has created a model designed to predict the amount of glacier loss up to the year 2100 and the ecosystems that will arise in their place.
Modeling the future of glaciers and the new ecosystems that will develop as deglaciation occursA team of geologists and geoscientists affiliated with several institutions in Switzerland and two in France, has created a model designed to predict the amount of glacier loss up to the year 2100 and the ecosystems that will arise in their place.
Weiterlesen »
 Decoding how molecules 'talk' to each other to develop new nanotechnologies -- ScienceDailyScientists recreate and compare molecular languages at the origin of life -- opening new doors for the development of novel nanotechnologies.
Decoding how molecules 'talk' to each other to develop new nanotechnologies -- ScienceDailyScientists recreate and compare molecular languages at the origin of life -- opening new doors for the development of novel nanotechnologies.
Weiterlesen »
 Kids Are 5 to 7 Times More Likely to Develop Lymphoma If They Live Near FrackingPennsylvania-based researchers identified the risk of cancer for children living within 1 mile of a fracking well.
Kids Are 5 to 7 Times More Likely to Develop Lymphoma If They Live Near FrackingPennsylvania-based researchers identified the risk of cancer for children living within 1 mile of a fracking well.
Weiterlesen »
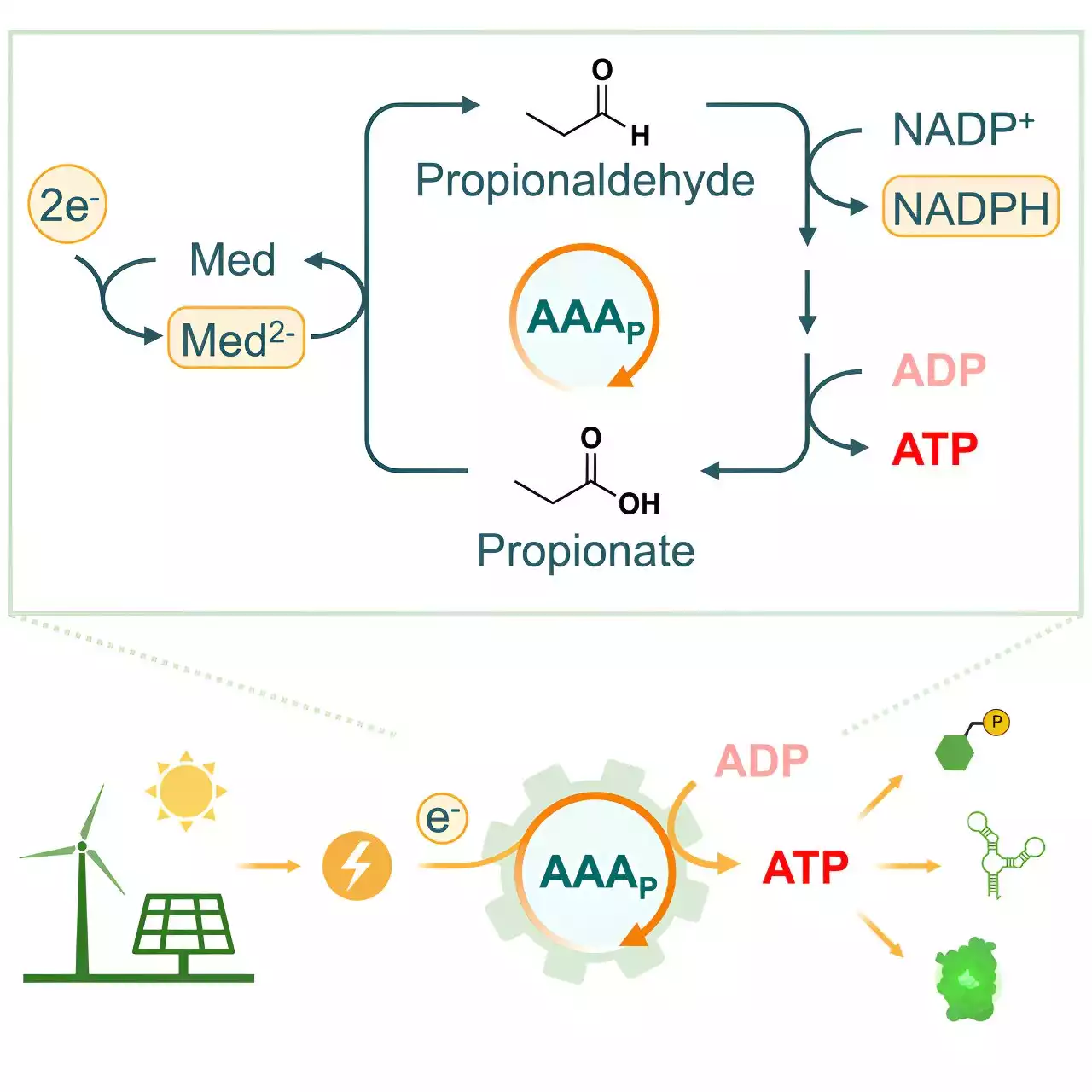 Scientists develop artificial metabolic pathway that uses electricity to produce ATPWhen nature performs chemical reactions to create energy-rich compounds from simple molecules, it requires energy. So far, it has not been possible to use human-made electricity to drive these biochemical processes.
Scientists develop artificial metabolic pathway that uses electricity to produce ATPWhen nature performs chemical reactions to create energy-rich compounds from simple molecules, it requires energy. So far, it has not been possible to use human-made electricity to drive these biochemical processes.
Weiterlesen »