How does the belief that vaccination will end the COVID-19 pandemic relate to vaccination intent? CDCgov SARSCoV2 COVID19 Vaccination Vaccine Intent
By Bhavana KunkalikarJul 11 2022Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study published in the Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, researchers explored intent and belief in coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in the Netherlands.
The team conducted a survey between 12 March and 22 March 2021 when 1.5 million out of 17.5 million Netherlands residents were either partly or fully vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 infections. The online survey was sent to 6810 individuals aged 18 years and above. The sample chosen for the survey was deemed as representative of the general Dutch population according to demographic characteristics.
Related StoriesThe team also assessed the extent to which the beliefs were responsible for the variation in vaccination intentions and identified the specific beliefs that determined vaccination intentions. This was achieved by performing a regression analysis using Random Forest , a machine learning method that facilitated regression and classification according to an ensemble of decision trees.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
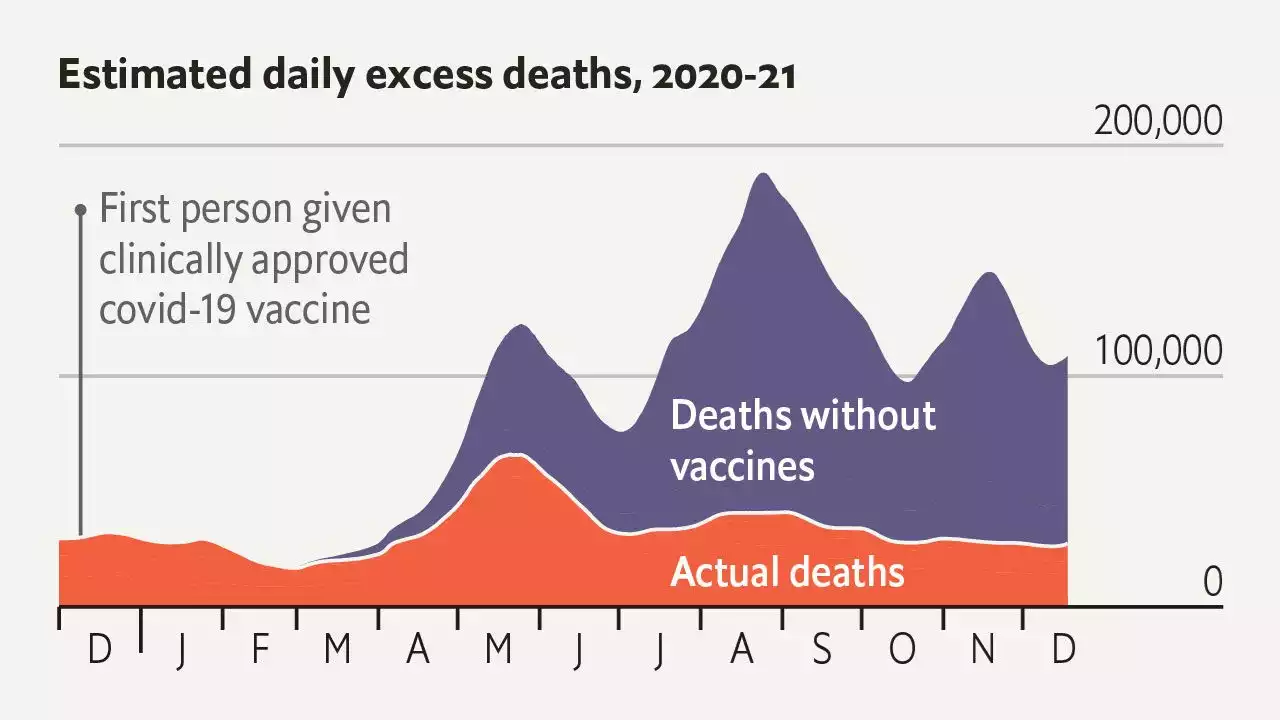 Covid-19 vaccines saved an estimated 20m lives during their first yearAs bad as the past 18 months have been, they would have been worse without vaccines—perhaps about 2.7 times worse
Covid-19 vaccines saved an estimated 20m lives during their first yearAs bad as the past 18 months have been, they would have been worse without vaccines—perhaps about 2.7 times worse
Weiterlesen »
 Key characteristics impacting survival of COVID-19 extracorporeal membrane oxygenation - Critical CareBackground Severe COVID-19 induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) often requires extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Recent German health insurance data revealed low ICU survival rates. Patient characteristics and experience of the ECMO center may determine intensive care unit (ICU) survival. The current study aimed to identify factors affecting ICU survival of COVID-19 ECMO patients. Methods 673 COVID-19 ARDS ECMO patients treated in 26 centers between January 1st 2020 and March 22nd 2021 were included. Data on clinical characteristics, adjunct therapies, complications, and outcome were documented. Block wise logistic regression analysis was applied to identify variables associated with ICU-survival. Results Most patients were between 50 and 70 years of age. PaO2/FiO2 ratio prior to ECMO was 72 mmHg (IQR: 58–99). ICU survival was 31.4%. Survival was significantly lower during the 2nd wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. A subgroup of 284 (42%) patients fulfilling modified EOLIA criteria had a higher survival (38%) (p = 0.0014, OR 0.64 (CI 0.41–0.99)). Survival differed between low, intermediate, and high-volume centers with 20%, 30%, and 38%, respectively (p = 0.0024). Treatment in high volume centers resulted in an odds ratio of 0.55 (CI 0.28–1.02) compared to low volume centers. Additional factors associated with survival were younger age, shorter time between intubation and ECMO initiation, BMI | 35 (compared to | 25), absence of renal replacement therapy or major bleeding/thromboembolic events. Conclusions Structural and patient-related factors, including age, comorbidities and ECMO case volume, determined the survival of COVID-19 ECMO. These factors combined with a more liberal ECMO indication during the 2nd wave may explain the reasonably overall low survival rate. Careful selection of patients and treatment in high volume ECMO centers was associated with higher odds of ICU survival. Trial registration Registered in the German Clinical Trials Re
Key characteristics impacting survival of COVID-19 extracorporeal membrane oxygenation - Critical CareBackground Severe COVID-19 induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) often requires extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Recent German health insurance data revealed low ICU survival rates. Patient characteristics and experience of the ECMO center may determine intensive care unit (ICU) survival. The current study aimed to identify factors affecting ICU survival of COVID-19 ECMO patients. Methods 673 COVID-19 ARDS ECMO patients treated in 26 centers between January 1st 2020 and March 22nd 2021 were included. Data on clinical characteristics, adjunct therapies, complications, and outcome were documented. Block wise logistic regression analysis was applied to identify variables associated with ICU-survival. Results Most patients were between 50 and 70 years of age. PaO2/FiO2 ratio prior to ECMO was 72 mmHg (IQR: 58–99). ICU survival was 31.4%. Survival was significantly lower during the 2nd wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. A subgroup of 284 (42%) patients fulfilling modified EOLIA criteria had a higher survival (38%) (p = 0.0014, OR 0.64 (CI 0.41–0.99)). Survival differed between low, intermediate, and high-volume centers with 20%, 30%, and 38%, respectively (p = 0.0024). Treatment in high volume centers resulted in an odds ratio of 0.55 (CI 0.28–1.02) compared to low volume centers. Additional factors associated with survival were younger age, shorter time between intubation and ECMO initiation, BMI | 35 (compared to | 25), absence of renal replacement therapy or major bleeding/thromboembolic events. Conclusions Structural and patient-related factors, including age, comorbidities and ECMO case volume, determined the survival of COVID-19 ECMO. These factors combined with a more liberal ECMO indication during the 2nd wave may explain the reasonably overall low survival rate. Careful selection of patients and treatment in high volume ECMO centers was associated with higher odds of ICU survival. Trial registration Registered in the German Clinical Trials Re
Weiterlesen »
 Covid-19 in the UKCovid infections in the UK have continued to rise, the latest weekly Office for National Statistics (ONS) figures suggest.
Covid-19 in the UKCovid infections in the UK have continued to rise, the latest weekly Office for National Statistics (ONS) figures suggest.
Weiterlesen »
 Speaking COVID-19: supporting COVID-19 communication and engagement efforts with people from culturally and linguistically diverse communities - BMC Public HealthBackground Since the emergence of COVID-19, issues have been raised regarding the approach used to engage with Culturally and Linguistically Diverse (CaLD) communities during this public health crisis. This study aimed to understand the factors impacting communication and engagement efforts during the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of crucial CaLD community stakeholders and opinion leaders. Methods Forty-six semi-structured telephone interviews were undertaken with key stakeholders who have an active role (established before the pandemic) in delivering services and other social support to CaLD communities in Australia. Results Seven key themes emerged: (1) the digital divide and how to connect with people; (2) information voids being filled by international material; (3) Differentiating established with new and emerging communities’ needs; (4) speaking COVID-19; (5) ineffectiveness of direct translations of English language resources; (6) coordination is needed to avoid duplication and address gaps and (7) recognising the improvements in governments’ approach. Conclusion Alliances must be set up that can be activated in the future to reduce issues around resource development, translation, and dissemination of messages to minimise gaps in the response. Financial assistance must be provided in a timely way to community organisations to support the development and dissemination of culturally appropriate communication materials.
Speaking COVID-19: supporting COVID-19 communication and engagement efforts with people from culturally and linguistically diverse communities - BMC Public HealthBackground Since the emergence of COVID-19, issues have been raised regarding the approach used to engage with Culturally and Linguistically Diverse (CaLD) communities during this public health crisis. This study aimed to understand the factors impacting communication and engagement efforts during the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of crucial CaLD community stakeholders and opinion leaders. Methods Forty-six semi-structured telephone interviews were undertaken with key stakeholders who have an active role (established before the pandemic) in delivering services and other social support to CaLD communities in Australia. Results Seven key themes emerged: (1) the digital divide and how to connect with people; (2) information voids being filled by international material; (3) Differentiating established with new and emerging communities’ needs; (4) speaking COVID-19; (5) ineffectiveness of direct translations of English language resources; (6) coordination is needed to avoid duplication and address gaps and (7) recognising the improvements in governments’ approach. Conclusion Alliances must be set up that can be activated in the future to reduce issues around resource development, translation, and dissemination of messages to minimise gaps in the response. Financial assistance must be provided in a timely way to community organisations to support the development and dissemination of culturally appropriate communication materials.
Weiterlesen »
 Lorraine Kelly forced to miss ITV show after testing positive for Covid-19No Lorraine Kelly this morning as she tests positive for Covid-19 - We hope you get better soon Lorraine 💖
Lorraine Kelly forced to miss ITV show after testing positive for Covid-19No Lorraine Kelly this morning as she tests positive for Covid-19 - We hope you get better soon Lorraine 💖
Weiterlesen »
 How the COVID-19 pandemic affected mental health and wellbeing, key determinants of health, and health inequitiesHow the COVID-19 pandemic affected mental health and wellbeing, key determinants of health, and health inequities medrxivpreprint UMontreal USherbrooke UQAR mentalhealth wellbeing COVID19 coronavirus covid pandemic
How the COVID-19 pandemic affected mental health and wellbeing, key determinants of health, and health inequitiesHow the COVID-19 pandemic affected mental health and wellbeing, key determinants of health, and health inequities medrxivpreprint UMontreal USherbrooke UQAR mentalhealth wellbeing COVID19 coronavirus covid pandemic
Weiterlesen »
