The power of machine learning in prostatecancer imaging
B). The 1000th step was predicted with a DSC of 0.9574 and an accuracy of 0.9945. The 3000th step was predicted with a DSC of 0.9991 and an accuracy of 0.9988. Although the model over-fit the training data, we still saw an increase in the prediction accuracy on synthetic images with more epochs of training and decided to use the 3000th step model for this analysis.
. The accuracy for groups were 62%, 55%, and 53%, respectively. A Pearson’s Chi-square test showed no significant association between experience level and the number of correct predictions , no association between experience level and the number of false negatives , and no association between experience level and the number of false positives ; however, a significant association was found for concordance within groups when all groups were considered.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Molly-Mae Hague admits she 'wasn't prepared' for how hard motherhood would beHowever, the Love Island star has insisted Bambi has made her relationship with Tommy stronger.
Molly-Mae Hague admits she 'wasn't prepared' for how hard motherhood would beHowever, the Love Island star has insisted Bambi has made her relationship with Tommy stronger.
Weiterlesen »
 Gary Lucy announces gender of baby with ex Laura AndersonGary Lucy has excitedly announced he is having a baby girl with ex-girlfriend Laura Anderson.
Gary Lucy announces gender of baby with ex Laura AndersonGary Lucy has excitedly announced he is having a baby girl with ex-girlfriend Laura Anderson.
Weiterlesen »
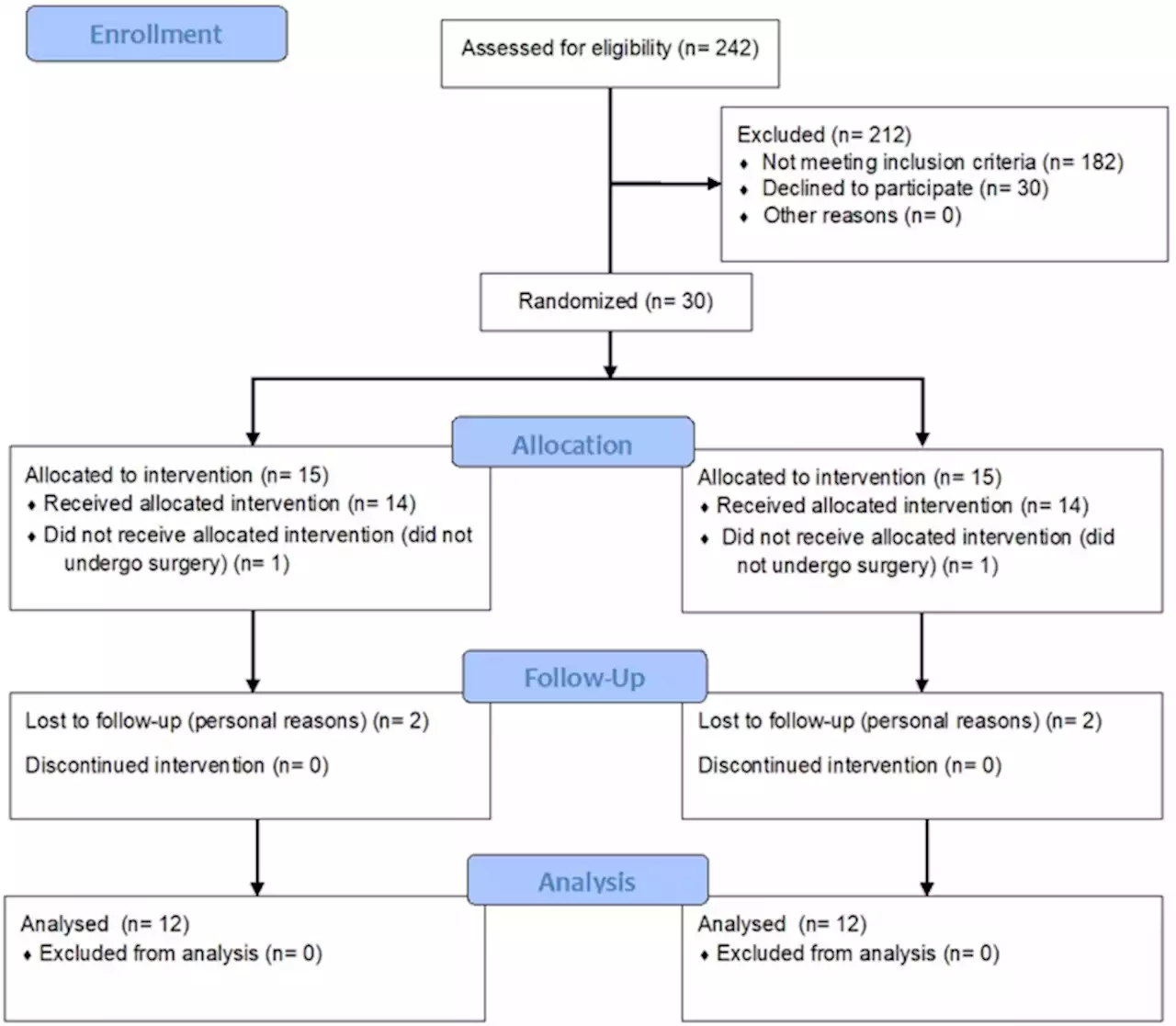 Exercise modifies hypothalamic connectivity and brain functional networks in women after bariatric surgery: a randomized clinical trial - International Journal of ObesityInternational Journal of Obesity - Exercise modifies hypothalamic connectivity and brain functional networks in women after bariatric surgery: a randomized clinical trial
Exercise modifies hypothalamic connectivity and brain functional networks in women after bariatric surgery: a randomized clinical trial - International Journal of ObesityInternational Journal of Obesity - Exercise modifies hypothalamic connectivity and brain functional networks in women after bariatric surgery: a randomized clinical trial
Weiterlesen »
 Pierce Brosnan's model son Dylan looks so different with short hairPierce Brosnan's son Dylan is known for his luscious long locks, however the model hasn't always had them so long – check out this unearthed photo
Pierce Brosnan's model son Dylan looks so different with short hairPierce Brosnan's son Dylan is known for his luscious long locks, however the model hasn't always had them so long – check out this unearthed photo
Weiterlesen »
 Application of Artificial Intelligence to the Monitoring of Medication Adherence for Tuberculosis Treatment in Africa: Algorithm Development and ValidationBackground: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications based on advanced deep learning methods in image recognition tasks can increase efficiency in the monitoring of medication adherence through automation. AI has sparsely been evaluated for the monitoring of medication adherence in clinical settings. However, AI has the potential to transform the way health care is delivered even in limited-resource settings such as Africa. Objective: We aimed to pilot the development of a deep learning model for simple binary classification and confirmation of proper medication adherence to enhance efficiency in the use of video monitoring of patients in tuberculosis treatment. Methods: We used a secondary data set of 861 video images of medication intake that were collected from consenting adult patients with tuberculosis in an institutional review board–approved study evaluating video-observed therapy in Uganda. The video images were processed through a series of steps to prepare them for use in a training model. First, we annotated videos using a specific protocol to eliminate those with poor quality. After the initial annotation step, 497 videos had sufficient quality for training the models. Among them, 405 were positive samples, whereas 92 were negative samples. With some preprocessing techniques, we obtained 160 frames with a size of 224 × 224 in each video. We used a deep learning framework that leveraged 4 convolutional neural networks models to extract visual features from the video frames and automatically perform binary classification of adherence or nonadherence. We evaluated the diagnostic properties of the different models using sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, and precision. The area under the curve (AUC) was used to assess the discriminative performance and the speed per video review as a metric for model efficiency. We conducted a 5-fold internal cross-validation to determine the diagnostic and discriminative performance of the models. We did not conduct exter
Application of Artificial Intelligence to the Monitoring of Medication Adherence for Tuberculosis Treatment in Africa: Algorithm Development and ValidationBackground: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications based on advanced deep learning methods in image recognition tasks can increase efficiency in the monitoring of medication adherence through automation. AI has sparsely been evaluated for the monitoring of medication adherence in clinical settings. However, AI has the potential to transform the way health care is delivered even in limited-resource settings such as Africa. Objective: We aimed to pilot the development of a deep learning model for simple binary classification and confirmation of proper medication adherence to enhance efficiency in the use of video monitoring of patients in tuberculosis treatment. Methods: We used a secondary data set of 861 video images of medication intake that were collected from consenting adult patients with tuberculosis in an institutional review board–approved study evaluating video-observed therapy in Uganda. The video images were processed through a series of steps to prepare them for use in a training model. First, we annotated videos using a specific protocol to eliminate those with poor quality. After the initial annotation step, 497 videos had sufficient quality for training the models. Among them, 405 were positive samples, whereas 92 were negative samples. With some preprocessing techniques, we obtained 160 frames with a size of 224 × 224 in each video. We used a deep learning framework that leveraged 4 convolutional neural networks models to extract visual features from the video frames and automatically perform binary classification of adherence or nonadherence. We evaluated the diagnostic properties of the different models using sensitivity, specificity, F1-score, and precision. The area under the curve (AUC) was used to assess the discriminative performance and the speed per video review as a metric for model efficiency. We conducted a 5-fold internal cross-validation to determine the diagnostic and discriminative performance of the models. We did not conduct exter
Weiterlesen »
