Exposing the evolutionary weak spots of the humangenome CSHL NatureComms
. Interestingly, despite their extreme levels of cross-species conservation, UCNEs show only modest levels of ultraselection, with= 0.09. This observation suggests that what is unusual about these elements is not the strength of selection acting on them , but instead the uniformity of selection acting at each nucleotide . Notably, HARs display only slightly lower levels of ultraselection than UCNEs and levels comparable to those of conserved sequences in introns.
Our assumption is that any point mutation at these ultraselected sites will be strongly deleterious, and simulations indicate that the detected sites are indeed subject to extreme purifying selection . Thus, if we multiply the expected numbers of sites by twice the estimated per-generation, per-nucleotide mutation rate , we obtain expected numbers of de novo strongly deleterious mutations per potential zygote . By this method, we estimate 0.258 ± 0.
. The expected number of strongly deleterious mutations per potential zygote increases to 0.505 ± 0.003, of which 0.12 fall in CDSs. Taking these calculations together, we estimate a range of 0.26–0.51 strongly deleterious mutations per potential zygote, implying a high genetic burden but one that appears to be roughly compatible with other lines of evidence .
We performed a parallel analysis using INSIGHT, to estimate the numbers and distribution of more weakly deleterious mutations . In this case, we estimate that 3.2% of sites are under selection and the expected number ofdeleterious mutations per fertilization is 2.21. The fraction of deleterious mutations from CDS is 22%, with most of the remainder coming from introns and intergenic regions. lncRNAs andUTRs also make significant contributions.
Österreich Neuesten Nachrichten, Österreich Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
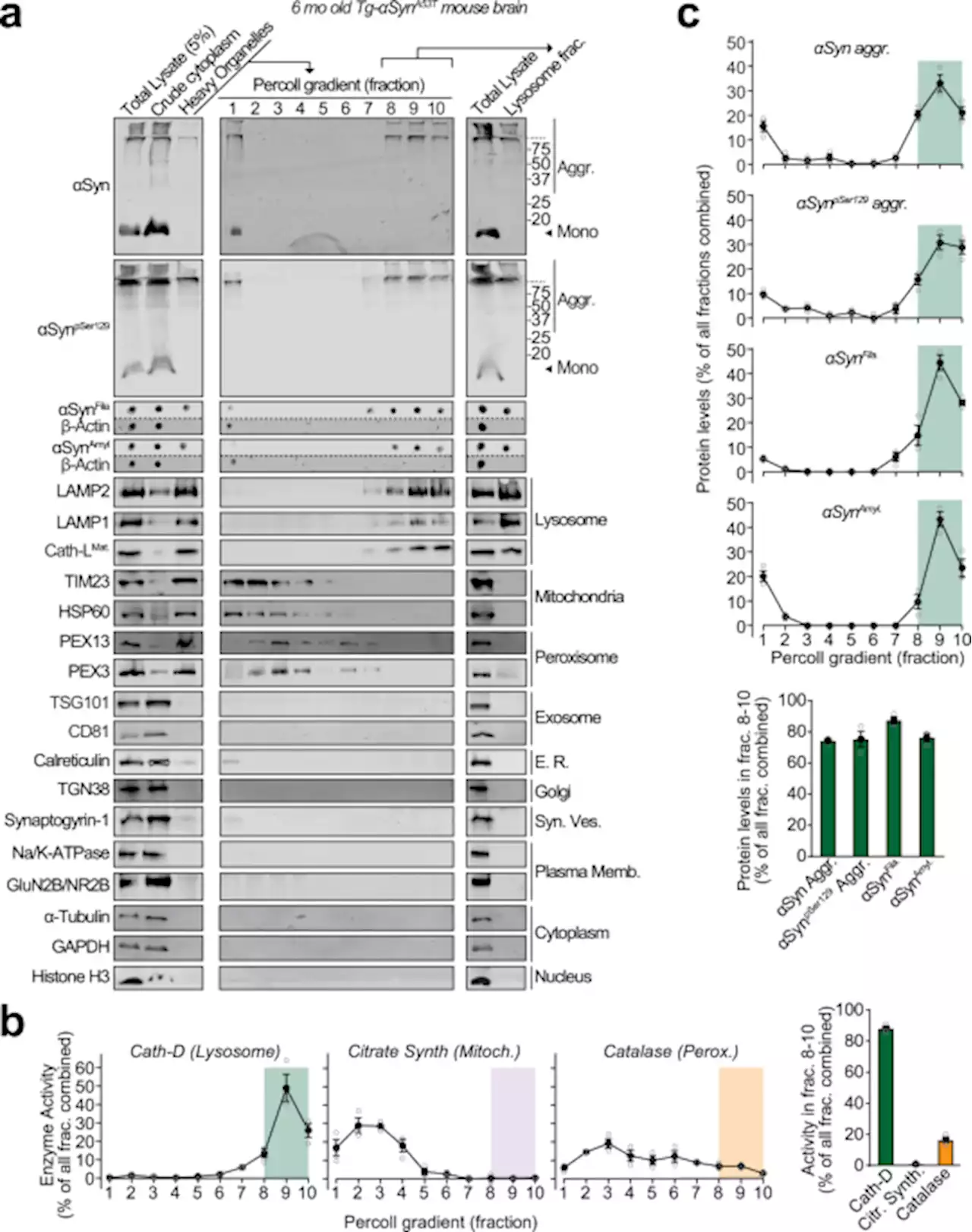 Lysosomal exocytosis releases pathogenic α-synuclein species from neurons in synucleinopathy models - Nature CommunicationsRelease of α-synuclein aggregates by neurons instigates spread of pathology in synucleinopathies, but the mechanism remains unclear. Here the authors show that neuronally generated α-synuclein aggregates accumulate within neuronal lysosomes and are released via SNARE-dependent lysosomal exocytosis.
Lysosomal exocytosis releases pathogenic α-synuclein species from neurons in synucleinopathy models - Nature CommunicationsRelease of α-synuclein aggregates by neurons instigates spread of pathology in synucleinopathies, but the mechanism remains unclear. Here the authors show that neuronally generated α-synuclein aggregates accumulate within neuronal lysosomes and are released via SNARE-dependent lysosomal exocytosis.
Weiterlesen »
 Differential dysregulation of granule subsets in WASH-deficient neutrophil leukocytes resulting in inflammation - Nature CommunicationsResponsive exocytosis in neutrophil leukocytes involves actin depolymerisation-dependent sequential release of gelatinase granules, then strongly pro-inflammatory azurophilic granules. Here authors show that the actin nucleator protein WASH facilitates the initial step of innate immune activation by gelatinase granules while inhibiting release of pro-inflammatory granules.
Differential dysregulation of granule subsets in WASH-deficient neutrophil leukocytes resulting in inflammation - Nature CommunicationsResponsive exocytosis in neutrophil leukocytes involves actin depolymerisation-dependent sequential release of gelatinase granules, then strongly pro-inflammatory azurophilic granules. Here authors show that the actin nucleator protein WASH facilitates the initial step of innate immune activation by gelatinase granules while inhibiting release of pro-inflammatory granules.
Weiterlesen »
 'Well-loved' dad killed in three-vehicle crash near golf club'Ray by name Ray by nature, a ray of sunshine and love'
'Well-loved' dad killed in three-vehicle crash near golf club'Ray by name Ray by nature, a ray of sunshine and love'
Weiterlesen »
 Women in Iran are “bolder and bolder” in fight for equality says Tara Sepehri Far, Human Rights Watch'I can't recall protests of this scale in demand for women's rights and dignity in recent years'. Tara Sepehri Far, Human Rights Watch tells JackieLongC4 that women are becoming 'bolder and bolder' in the fight for equality.
Women in Iran are “bolder and bolder” in fight for equality says Tara Sepehri Far, Human Rights Watch'I can't recall protests of this scale in demand for women's rights and dignity in recent years'. Tara Sepehri Far, Human Rights Watch tells JackieLongC4 that women are becoming 'bolder and bolder' in the fight for equality.
Weiterlesen »
 Generation of a CRISPR activation mouse that enables modelling of aggressive lymphoma and interrogation of venetoclax resistance - Nature CommunicationsModelling of aggressive lymphomas, such as double hit lymphoma, has been challenging. Here the authors engineer a CRISPR activation mouse to enable the generation of these aggressive lymphomas and identify the pro-survival BCL-2 protein A1 as a venetoclax resistance factor.
Generation of a CRISPR activation mouse that enables modelling of aggressive lymphoma and interrogation of venetoclax resistance - Nature CommunicationsModelling of aggressive lymphomas, such as double hit lymphoma, has been challenging. Here the authors engineer a CRISPR activation mouse to enable the generation of these aggressive lymphomas and identify the pro-survival BCL-2 protein A1 as a venetoclax resistance factor.
Weiterlesen »
